In Accounting and Finance, Equity represents the value of the shareholders’ or business owner’s stake in the business. Equity accounts have a normal credit balance. Equity increases on the credit side and decreases on the debit side.
Equity is listed on the Balance Sheet. Changes to Equity are calculated on the Statement of Owner’s Equity or Statement of Shareholders’ Equity or Statement of Retained Earnings.
Examples of Equity accounts are Owner’s Equity, Stockholders’ Equity, Shareholders’ Equity, and Common Stock.

What are Some Examples of Equity Accounts?
This table shows a list of common liabilities businesses use to track the amounts owed by the business.
| Common Stock | Retained Earnings |
| Preferred Stock | Additional Paid in Capital |
| Owner’s Name, Equity or Capital | Partner’s Name, Equity or Capital |
| Member’s Name, Equity or Capital | Unrealized Gains |
| Owner’s Name, Distribution | Owner’s Name, Withdrawals or Drawing |
| Dividends | Member’s Name, Distribution |
| Treasury Stock | Unrealized Losses |
What Accounts are Used to Record Increases in Equity?
The following Equity accounts are used to track increases in Equity:
| Common Stock | Retained Earnings |
| Preferred Stock | Additional Paid in Capital |
| Owner’s Name, Equity or Capital | Partner’s Name, Equity or Capital |
| Member’s Name, Equity or Capital | Unrealized Gains |
What Accounts are Used to Record Decreases in Equity?
The following accounts are used to track decreases in owner’s or shareholder’s equity.
| Owner’s Name, Distribution | Owner’s Name, Withdrawals or Drawing |
| Dividends | Member’s Name, Distribution |
| Treasury Stock | Unrealized Losses |
What is the Difference Between Equity and Capital?
Capital is a subcategory of equity. Capital represents an owner’s investment of assets into the business. For example, when the business started the owner contributed cash and equipment to start the business.
Equity represents the difference between Assets and Liabilities. If a business sells all of its assets and pays off all its debts (liabilities), the amount remaining is the owner’s share (equity) of the business.
A business owner’s capital increases when they invest more money or other assets into the company. A business owner’s equity increases when there are profits in the business.
Total equity includes Capital + Retained Earnings – Dividends (Withdrawals)
What is Retained Earnings?
Retained Earnings represents the cumulative profits and losses in a business, net of Dividends. As a business has profits and losses over years, Retained Earnings increases or decreases as in this example:
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| Net Income | 10,000 | 15,000 | -1,000 |
| Dividends | -100 | -200 | 0 |
| Current Year Earnings | 9,900 | 14,800 | -1,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 9,900 | 24,700 | 23,700 |
How is Equity Listed on the Balance Sheet?
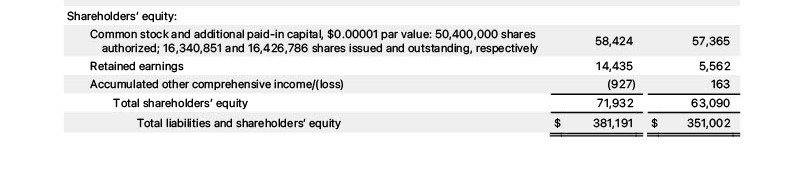
On the Balance Sheet, equity is broken down by type of equity, including owner’s original investment, retained earnings, common stock, preferred stock, dividends, and treasury stock. Changes in equity are tracked on the Statement of Owner’s Equity or Statement of Shareholders’ Equity or Statement of Retained Earnings. Those amounts are then summarized on the Balance Sheet in the Equity section.
Here is an example of the equity section of the Balance Sheet from Apple:
What is the Statement of Owner’s Equity? What is the Statement of Shareholder’s Equity? What is the Statement of Retained Earnings?
For a more in depth understanding of the Statement of Owner’s Equity, watch this video:
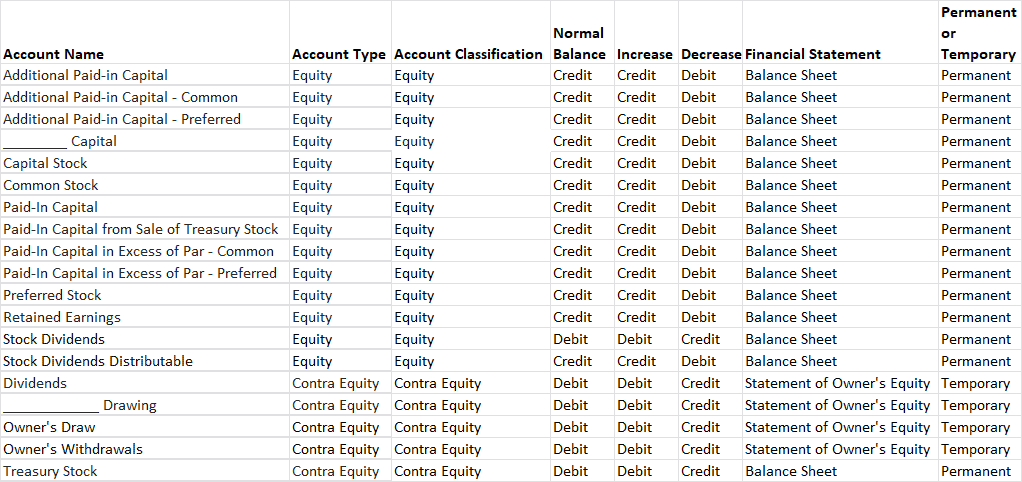
Chart of Accounts Listing of Typical Equity Accounts
For more information about how equity is reported on Financial Statements, check out these articles:
-
How to Know What to Debit and What to Credit in Accounting
If you’re not used to speaking the language of accounting, understanding debits and credits can seem confusing at first. In this article, we will walk through step-by-step all the building
-
How to Analyze Accounting Transactions, Part One
The first four chapters of Financial Accounting or Principles of Accounting I contain the foundation for all accounting chapters and classes to come. It’s critical for accounting students to get
-
What is an Asset?
An Asset is a resource owned by a business. A resource may be a physical item such as cash, inventory, or a vehicle. Or a resource may be an intangible
-
What is a Liability?
A Liability is a financial obligation by a person or business to pay for goods or services at a later date than the date of purchase. An example of a
-
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the income generated by a business in the normal course of operations. It represents the sale of goods and services to customers or clients. For a non-profit organization,
-
What Does Prepaid Mean in Accounting?
In accounting, a Prepaid account represents cash expended prior to goods or services being received. Examples of Prepaid accounts are Prepaid Expense, Prepaid Rent, and Prepaid Insurance. A Prepaid account
-
What is Equity in Accounting and Finance?
In Accounting and Finance, Equity represents the value of the shareholders’ or business owner’s stake in the business. Equity accounts have a normal credit balance. Equity increases on the credit
-
What is Treasury Stock?
Treasury Stock represents a corporation’s stocks that were previously issued and sold to shareholders. The corporation reacquires the stock by purchasing the stock from shareholders. Treasury Stock reduces the number
-
What is Stockholders’ Equity?
Stockholders’ Equity is the difference between what a corporation owns (Assets) and what a corporation owes (Liabilities). Stockholders’ Equity is made up of Contributed Capital and Earned Capital. Contributed Capital
-
What is Paid in Capital?
What is Contributed or Paid-in Capital? Contributed Capital is also called Paid-in Capital. It includes any amounts “contributed” or “paid in” by investors or stockholders through purchasing of stocks or
-
What are Dividends? | Accounting Student Guide
What is a Dividend? A Dividend is a payout of earnings by a corporation to its stockholders. Dividends can be cash dividends or stock dividends. A dividend is paid per
-
What are Stock Splits?
A stock split occurs when a corporation’s board of directors decides to divide one share of stock into multiple shares. For example, a two-for-one stock split means that one share