A Liability is a financial obligation by a person or business to pay for goods or services at a later date than the date of purchase. An example of a liability for a business is Accounts Payable. The obligation may be short-term, paid within a year, or long-term, paid over multiple years. Liabilities have a normal credit balance. Liabilities are listed on the Balance Sheet. Other examples of liabilities include Notes Payable, Mortgage Payable, Salaries Payable, Unearned Rent, and Unearned Revenue.

What are Some Examples of Liabilities?
This table shows a list of common liabilities businesses use to track the amounts owed by the business.
| Accounts Payable | Payroll Taxes Payable |
| Accrued Liabilities | Customer Deposits |
| Accrued Wages | Unearned Revenue |
| Wages Payable | Unearned Rent |
| Salaries Payable | Sales Tax Payable |
| Interest Payable | Deferred Revenue |
| Note Payable–short-term | Current Portion of Long-term Debt |
| Bonds Payable | Mortgage Payable |
| Note Payable–long-term | Pension Liability |
What are the Types of Liabilities?
Liabilities are divided into two broad groups:
- Current Liabilities
- Non-current or Long-term Liabilities
Current Liabilities are considered to be short-term liabilities (less than a year). Non-current liabilities are long-term liabilities expected to be paid over a period longer than one year.
Below are examples of liabilities classified as Current Liabilities (short-term liabilities):
| Accounts Payable | Payroll Taxes Payable |
| Accrued Liabilities | Customer Deposits |
| Accrued Wages | Unearned Revenue |
| Wages Payable | Unearned Rent |
| Salaries Payable | Sales Tax Payable |
| Interest Payable | Deferred Revenue |
| Note Payable–short-term | Current Portion of Long-term Debt |
Below are examples of liabilities classified as Non-current Liabilities (long-term liabilities):
| Bonds Payable | Mortgage Payable |
| Note Payable–long-term | Pension Liability |
What is the Difference Between Current Liabilities and Long-term Liabilities?
A Current Liability is defined as a liability that is one that is expected to be paid within in one year or less (an operating cycle.) For more in depth information about Current Liabilities, watch this video:
A Long-term Liability is defined as a liability that is expected to be paid more than one year (multiple operating cycles.)
How are Liabilities Listed on the Balance Sheet
On the Balance Sheet, liabilities are generally listed in order of when payment is due, from shortest term to longest term. For example, Accounts Payable is expected to be paid with about 30 days, a 90-day Note Payable is expected to be paid in 90 days, and a five-year car loan is expected to be paid off over a period of five years. Liabilities are categorized on the Balance Sheet as Current or Long-term Liabilities.
On the Balance Sheet, the liabilities would be listed:
| Liabilities |
| Current Liabilities |
| Accounts Payable |
| Note Payable-short term |
| Long-term Liabilities |
| Car Loan |
| Total Liabilities |
Here is an example of the liability section of the Balance Sheet from Apple:
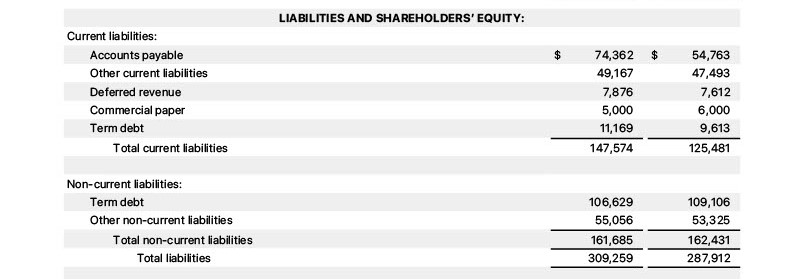
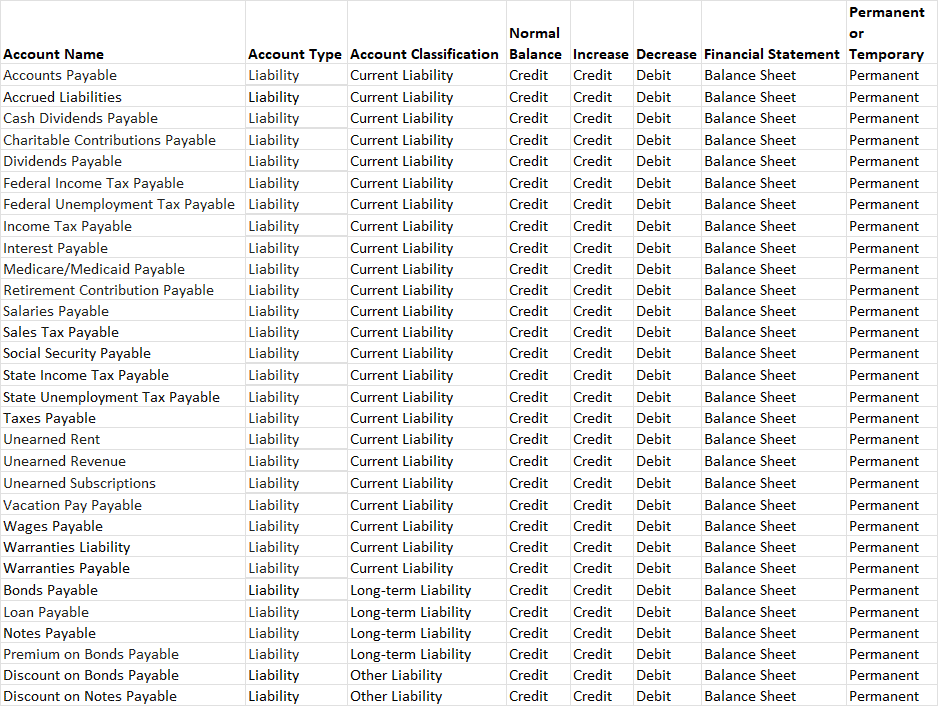
Chart of Account Listing for Typical Liability Accounts:
For more about long-term liabilities, check out this article:
-
So You Want to Start a Nonprofit…Consider This
Starting a nonprofit can be a fulfilling way to make a difference in the community, but it requires careful planning and consideration. Here are key points to consider before embarking
-
Tax Liability Accrual Explained
Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid. This is important for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting
-
Nonprofit Monthly Financial Close Process Overview
The monthly accounting close process for a nonprofit organization involves a series of steps to ensure accurate and up-to-date financial records. This process ensures that financial statements are prepared, reviewed,
-
Navigating Payroll Taxes for Nonprofits: Responsibilities and Compliance
Payroll taxes are the taxes that employers withhold from their employees’ wages and are required to remit to the appropriate government agencies. They include various taxes that fund government programs,
-
Understanding Form 990: Transparency and Accountability for Nonprofits
Form 990 is a reporting document filed by tax-exempt organizations in the United States with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It provides detailed information about the organization’s financial activities, governance,
-
Financial Disclosures for Affiliated Nonprofit Organizations
Disclosures related to revenue sharing, consolidated financial statements, noncontrolling interests, and related party transactions in the context of affiliated organizations within a nonprofit are crucial for transparency and accurate financial