An Income Statement is one of the major financial statements. It is also called a Profit and Loss Statement or a P&L. It shows the relationship between revenue (what a company makes for income) and expenses (what a company spends to make that income). The difference between revenue and expenses is profit or loss. When revenue is greater than expenses, the company has a profit. When revenue is less than expenses, the company has a loss.
What are the Income Statement Accounts?
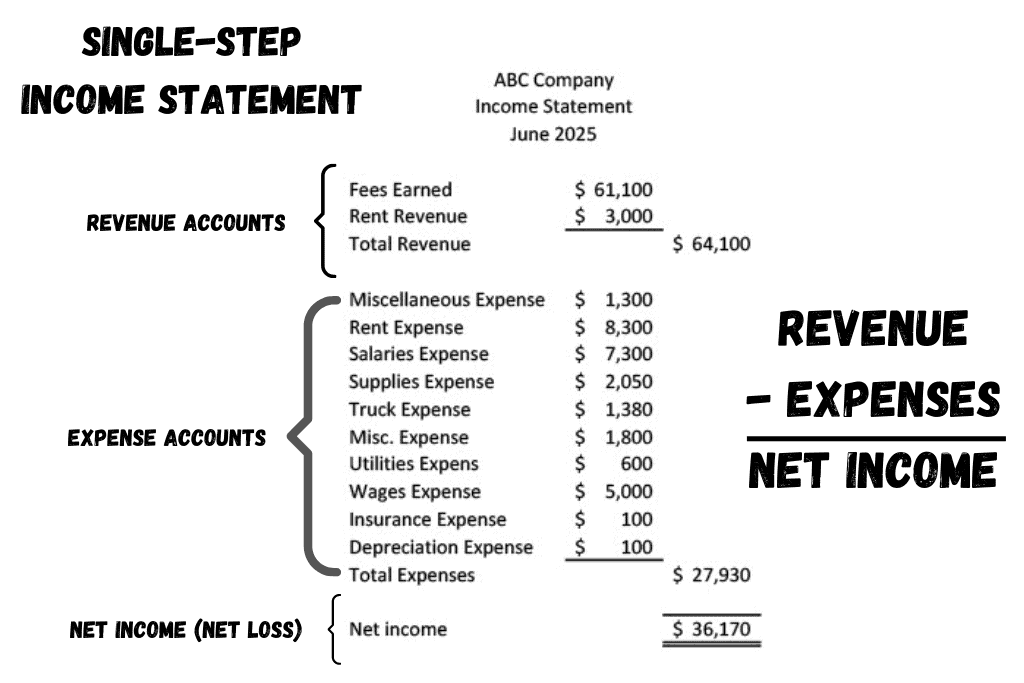
The Income Statement shows a listing of revenue and expense accounts.
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the income generated by a business in the normal course of operations. It represents the sale of goods and services to customers or clients. For a non-profit organization, revenue is the income generated by donations, grants, and programs. Revenue accounts have a normal credit balance. Revenue is listed on the Income Statement. Examples of Revenue accounts include Sales, Sales Revenue, Fees Earned, and Professional Fees.
When is Revenue Recorded?
Revenue is recorded when earned. When revenue is earned is based on the accounting method a company uses, cash basis or accrual basis. Under the Cash Basis method, revenue is earned when cash is received. Under the Accrual Basis method, revenue is earned when the work is done or the goods are delivered, regardless of when cash is received.
For businesses required to follow U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), the Accrual Basis of accounting is required.
For more information about Cash Basis vs. Accrual Basis accounting, watch this video:
What are Expenses?
An Expense represents a cost incurred in the making of revenue. Examples of Expenses are Rent, Insurance, cost of goods, and payroll. An expense is also used to record the reduction of value of an Asset. For example, Depreciation Expense is used to record the reduction in value of an Asset like a deliver van. An expense has a normal debit balance. Expenses are listed on the Income Statement.
When are Expenses Recorded?
Expenses are recorded when incurred, when they happen–goods are delivered, services are received. When an expense is considered “incurred” and recorded is based on the accounting method a company uses, cash basis or accrual basis.
Under the Cash Basis method, an expense is only incurred (recorded on the Income Statement) when cash is paid out.
Under the Accrual Basis method, an expense is recognized (recorded on the Income Statement) when the services are delivered or the goods are delivered, regardless of when cash is received.
For businesses required to follow U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), the Accrual Basis of accounting is required.
What is the Difference Between a Single-step Income Statement and a Multi-step Income Statement?
A single-step income statement and a multi-step income statement differ in the amount of categorizing of financial information found on the report. A single-step income statement shows Revenues and Expenses, and calculates Net Income. A multi-step income statement adds a sections for costs of goods sold and groups expenses into additional categories.
For more information about Single-step and Multi-step Income Statements, check out this article:
What is Cost of Goods Sold?
In accounting, Cost of Goods Sold is an account used to track the costs associated with the manufacture of a product, including cost of raw materials, direct labor, packaging, and other direct costs. Cost of Goods Sold does not include general or overhead costs for the business, such as rent, insurance, and office support.
Cost of Goods Sold is an expense account. It has a normal debit balance. It increases on the debit side and decreases on the credit side.
What is Cost of Merchandise Sold?
In accounting, Cost of Merchandise Sold is an account used to track the costs associated with the purchase of products for resale in a merchandising or retail business. Cost of Merchandise Sold does not include general or overhead costs for the business, such as rent, insurance, and office support.
Cost of Merchandise Sold is an expense account. It has a normal debit balance. It increases on the debit side and decreases on the credit side.
What is Gross Profit?
Gross Profit is the difference between Revenue and Cost of Merchandise Sold or Cost of Goods Sold. It shows how much a company has to spend to purchase or make the products or services it sells compared to the selling price of the product. For example, if an item sells for $10 and the cost of purchasing or manufacturing that item is $7, the company has a gross profit of $3 [$10 – $7 = $3]
Gross Profit is carefully tracked and managed to measure how much profit in a business comes from purchasing and selling a product. It is reported in a multi-step income statement in this format:
| Revenue | 10,000 | |
| Cost of Merchandise Sold | 7,000 | |
| Gross Profit | 3,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Rent Expense | 1,800 | |
| Insurance Expense | 500 | |
| Total Expenses | 2,300 | |
| Net Income | 700 |
What is Net Income?
In a business, Net Income is the difference between Revenue and Expenses. When the difference is positive (revenues are greater than expenses), the business has a profit or Net Income. When the difference is negative (expenses are greater than revenues), the business has a loss or Net Loss.
Why is an Income Statement Important?
An Income Statement shows whether a business is operating at a profit. It acts as the scoreboard for a business. Comparing Income Statements from month to month or year to year helps to spot trends and trouble areas. By continually measuring revenues, business owners and managers can see whether revenue is increasing or decreasing over time. Continually measuring expenses tracks whether expenses are increasing or decreasing, and which specific expenses are increasing. Monitoring the critical relationship between revenue and expenses helps to find ways to increase profits and revenues and decrease expenses (or re-allocate funds to different expenses.)
Like all financial statements, the Income Statement gives one view of the finances of a business. When the Income Statement, Statement of Owner’s Equity, Balance Sheet, and Statement of Cash Flow are examined separately and as a whole, a picture of the overall health and decisions of the company can come into focus.
For more information and examples about the Income Statement, watch this video:
For access to the example spreadsheet in the video, click this Google Drive link:
Income Statement Examples spreadsheet
-
What is Equity in Accounting and Finance?
In Accounting and Finance, Equity represents the value of the shareholders’ or business owner’s stake in the business. Equity accounts have a normal credit balance. Equity increases on the credit
-
Understanding Financial Statements | Accounting Student Guide
What is a Financial Statement? Financial Statements are a set of reports summarizing the activities of a business or organization. Much like a series of x-rays shows different views of
-
What is Treasury Stock?
Treasury Stock represents a corporation’s stocks that were previously issued and sold to shareholders. The corporation reacquires the stock by purchasing the stock from shareholders. Treasury Stock reduces the number
-
What is Stockholders’ Equity?
Stockholders’ Equity is the difference between what a corporation owns (Assets) and what a corporation owes (Liabilities). Stockholders’ Equity is made up of Contributed Capital and Earned Capital. Contributed Capital
-
What is Paid in Capital?
What is Contributed or Paid-in Capital? Contributed Capital is also called Paid-in Capital. It includes any amounts “contributed” or “paid in” by investors or stockholders through purchasing of stocks or
-
What is the Difference Between Debt Financing and Equity Financing?
When businesses needs funds to expand or grow the business, that capital can come from three sources: Funds from profits Funds from debt Funds from equity Funding business growth from

