Revenue is the income generated by a business in the normal course of operations. It represents the sale of goods and services to customers or clients. For a non-profit organization, revenue is the income generated by donations, grants, and programs. Revenue accounts have a normal credit balance. Revenue is listed on the Income Statement. Examples of Revenue accounts include Sales, Sales Revenue, Fees Earned, and Professional Fees.

What are Some Examples of Revenue Accounts?
This table shows a list of common revenue accounts businesses use to track the sources of revenue received by the business or non-profit.
| Sales | Sales Revenue |
| Rent Revenue | Dividend Revenue |
| Interest Revenue | Commission Income |
| Royalty Income | Investment Income |
| Professional Fees | Fees Earned |
| Tax Revenue | Grant Revenue |
| Donations | Program Revenue |
What is the Difference Between Operating and Non-operating Revenue?
Revenue can be divided into two broad groups:
- Operating Revenue
- Non-operating Revenue
Operating Revenue comes from the income generated by the day-to-day transactions of a business. For example, when a convenience store sells merchandise to customers or a lawyer sells services to a client.
Non-operating Revenue is generated from activities not related to the core business of the company. For example, if the convenience store sells a display counter it no longer needs. The revenue generated from the sale is classified as non-operating revenue. It is outside of the day-to-day core business transactions.
Below are examples of Revenue classified as Operating Revenue:
| Sales | Sales Revenue |
| Rent Revenue | Commission Income |
| Royalty Income | Fees Earned |
| Professional Fees | Retail Sales |
| Tax Revenue | Grant Revenue |
| Donations | Program Revenue |
Below are examples of Revenue classified as Non-operating Revenue:
| Interest Revenue | Dividend Revenue |
| Investment Income | Revenue from sale of assets |
The classification for Operating vs. Non-operating revenue is based on the individual business or organization and how it makes its revenue.
For example, a non-profit organization may have as its core revenue sources donations and grants, but it may also may rent out part of it’s office building to another organization. The rent revenue received is not part of the core business, therefore, it would likely be classified as non-operating revenue.
If a business has as it’s core business renting apartments or offices to clients, the rental revenue would be classified as Operating Revenue.
When is Revenue Recognized or Considered to be Earned?
When revenue is earned is based on the accounting method a company uses, cash basis or accrual basis. Under the Cash Basis method, revenue is earned when cash is received. Under the Accrual Basis method, revenue is earned when the work is done or the goods are delivered, regardless of when cash is received.
For businesses required to follow U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), the Accrual Basis of accounting is required.
For more information about GAAP, watch this video:
What is the Difference Cash Basis and Accrual Basis?
Under Cash Basis of accounting, revenue is considered to be earned (included in revenue on the income statement) when cash is received. Expenses are considered to be incurred (included in expenses on the income statement) when cash is paid out.
Under Accrual Basis of accounting, revenue is considered to be earned (included in revenue on the income statement) at the time the work is completed or the goods are delivered, regardless of when cash is received. Expenses are considered to be incurred (included in expenses on the income statement) when the services are received or goods are received, regardless of when cash is paid out.
For more information about Cash Basis vs Accrual Basis, watch this video:
What is the difference between Accrued Revenue and Deferred Revenue?
Accrued Revenue represents revenue earned but not yet received. An example of Accrued Revenue is a sale to a customer on account. The portion of the revenue earned in the current month in included in revenue, but the cash will be received in a later month. Accounts Receivable is generally the account used to track Accrued Revenue.
Deferred Revenue represents payments received prior to the work being done or the goods being delivered. The cash payment is recorded to a deferred or unearned revenue account (a liability) until it is earned, at which time it will be moved from the liability account to the revenue account.
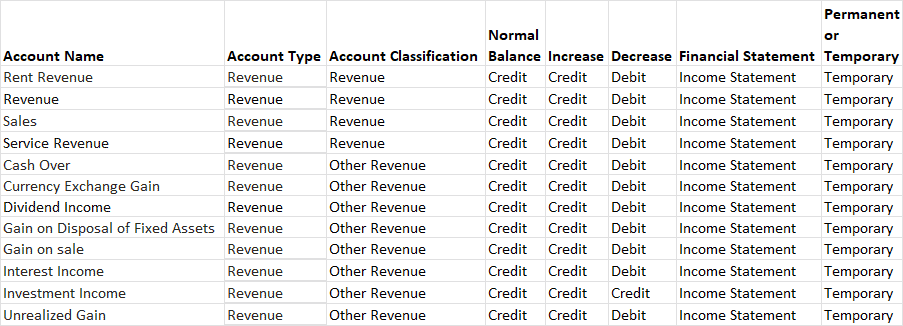
Chart of Account Listing of Typical Revenue Accounts:
For more information about how Revenue is reported on Financial Statements, check out this article:
-
How to Know What to Debit and What to Credit in Accounting
If you’re not used to speaking the language of accounting, understanding debits and credits can seem confusing at first. In this article, we will walk through step-by-step all the building
-
How to Analyze Accounting Transactions, Part One
The first four chapters of Financial Accounting or Principles of Accounting I contain the foundation for all accounting chapters and classes to come. It’s critical for accounting students to get
-
What is an Asset?
An Asset is a resource owned by a business. A resource may be a physical item such as cash, inventory, or a vehicle. Or a resource may be an intangible
-
What is a Liability?
A Liability is a financial obligation by a person or business to pay for goods or services at a later date than the date of purchase. An example of a
-
What is Revenue?
Revenue is the income generated by a business in the normal course of operations. It represents the sale of goods and services to customers or clients. For a non-profit organization,
-
What Does Prepaid Mean in Accounting?
In accounting, a Prepaid account represents cash expended prior to goods or services being received. Examples of Prepaid accounts are Prepaid Expense, Prepaid Rent, and Prepaid Insurance. A Prepaid account