An Intangible Asset is a long-term asset (or non-current asset), one that a business will hold for longer than a year. Like Tangible Assets, these are permanent items a business intends to own long-term (more than a year.) Intangible Assets include Copyrights, Goodwill, Trademarks, and Patents.
What is the Difference Between Intangible and Tangible Assets?
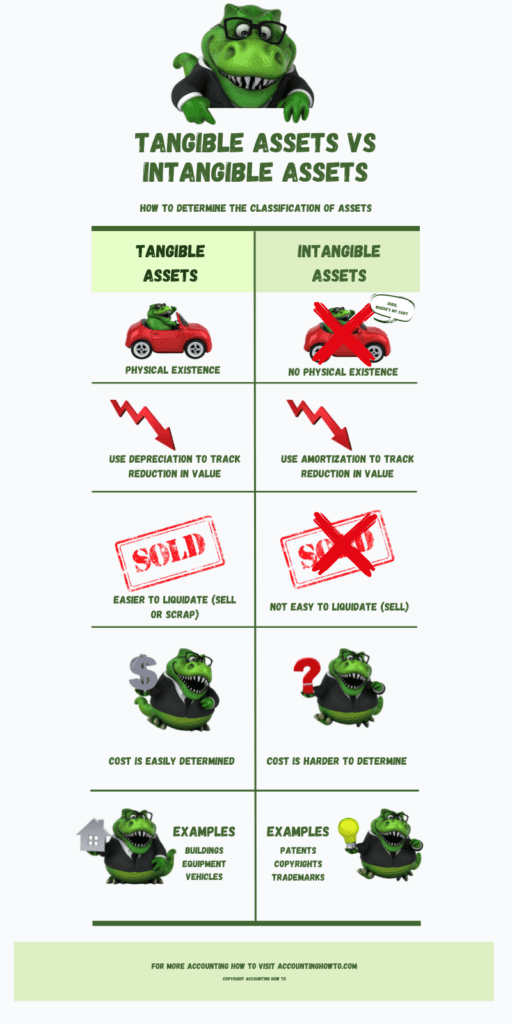
The difference between Tangible Assets and Intangible Assets is that Intangible Assets are not physical assets. Examples of Intangible Assets are Copyrights, Goodwill, Trademarks, and Patents. They provide value for a business by creating a competitive advantage. Intangible Assets may lose value over time and as such they are amortized to track the reduction in value. (Amortization on an Intangible Asset is like depreciation on Fixed Assets.)
A Tangible Asset is a long-term asset (non-current asset), on that a business will hold for longer than a year. A tangible asset is an asset that has a physical presence, is expected to be used to create value for the business. Tangible Assets are usually referred to as Fixed Assets or Property, Plant, and Equipment (PP&E). Examples of Tangible Assets include vehicles, equipment, buildings, and land. Tangible Assets are generally depreciated over time (land is not depreciated.)
For a more in depth look at Intangible Assets, watch this video:
Is an Intangible Asset a Fixed Asset?
Intangible Assets and Fixed Assets are different types of assets. Intangible Assets and Fixed Assets are both classified as Non-current or Long-term Assets. Fixed Assets are assets that have physical form (trucks, buildings, equipment) and are depreciated over time. Intangible Assets do not have physical form (copyrights, trademarks, patents) and are amortized over time.
For a more in depth look at Assets including Intangible Assets, check out this article:
-
How Do Journal Entries Work in Accounting?
Journal entries are one of the most fundamental and essential concepts in accounting. A journal entry is a record of a transaction that affects a company’s financial statements. Journal entries
-
What is a Statement of Shareholders’ Equity?
The Statement of Shareholders’ Equity is one of the four major financial statements. The function of the Statement of Shareholders’ Equity is to show changes in the value of equity
-
Accounting for Notes Receivable | Accounting Student Guide
What is a Note Receivable? A note receivable is formal payment agreement between two or more people or entities. It is a promissory note that specifies: Who the note is
-
How to Post Journal Entries to the Ledger
When a Journal Entry is made to record a transaction, that Journal Entry is then entered (posted) in the accounts being impacted. For example, when rent is paid, in the
-
What is the Accounting Equation?
Before you can understand debits and credits, you’ll need a little background on the structure of accounting. It all starts with the Accounting Equation. The Accounting Equation is the foundation
-
What is Owner’s Draw (Owner’s Withdrawal) in Accounting?
Owner’s Draw or Owner’s Withdrawal is an account used to track when funds are taken out of the business by the business owner for personal use. Business owners may use

