In accounting, Cost of Goods Sold is an account used to track the costs associated with the manufacture of a product, including cost of raw materials, direct labor, packaging, and other direct costs. Cost of Goods Sold does not include general or overhead costs for the business, such as rent, insurance, and office support.
Cost of Goods Sold is an expense account. It has a normal debit balance. It increases on the debit side and decreases on the credit side.
In accounting software, Cost of Goods Sold has an account type called Cost of Goods Sold rather than an expense. This signifies to the software that this account will be used to calculate Gross Profit.
Cost of Goods Sold is sometimes called Cost of Merchandise Sold. Cost of Goods Sold is more likely to be used for manufacturing businesses. Cost of Merchandise Sold is more likely to be used for merchandising (retail) businesses.

What is Gross Profit?
Gross Profit is the difference between Revenue and Cost of Goods Sold. It shows how much a company has to spend to make the products compared to the selling price of the product. For example, if an item sells for $10 and the cost of manufacturing that item is $7, the company has a gross profit of $3 [$10 – $7 = $3]
Gross Profit is carefully tracked and managed to measure how much profit in a business comes from making and selling a product. It is reported in a multi-step income statement in this format:
| Revenue | 10,000 | |
| Cost of Good Sold | 7,000 | |
| Gross Profit | 3,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Rent Expense | 1,800 | |
| Insurance Expense | 500 | |
| Total Expenses | 2,300 | |
| Net Income | 700 |
In a business, Net Income is the difference between Revenue and Expenses. When the difference is positive (revenues are greater than expenses), the business has a profit or Net Income. When the difference is negative (expenses are greater than revenues), the business has a loss or Net Loss.
What is the Difference Between Gross Profit and Net Income?
Gross Profit is the difference between what a product or service is sold for (selling price or Revenue) and what it costs the company to make or purchase products for sale to customers (Cost of Good Sold.) Net Income is the difference between Gross Profit and the Operating Expenses of a business.
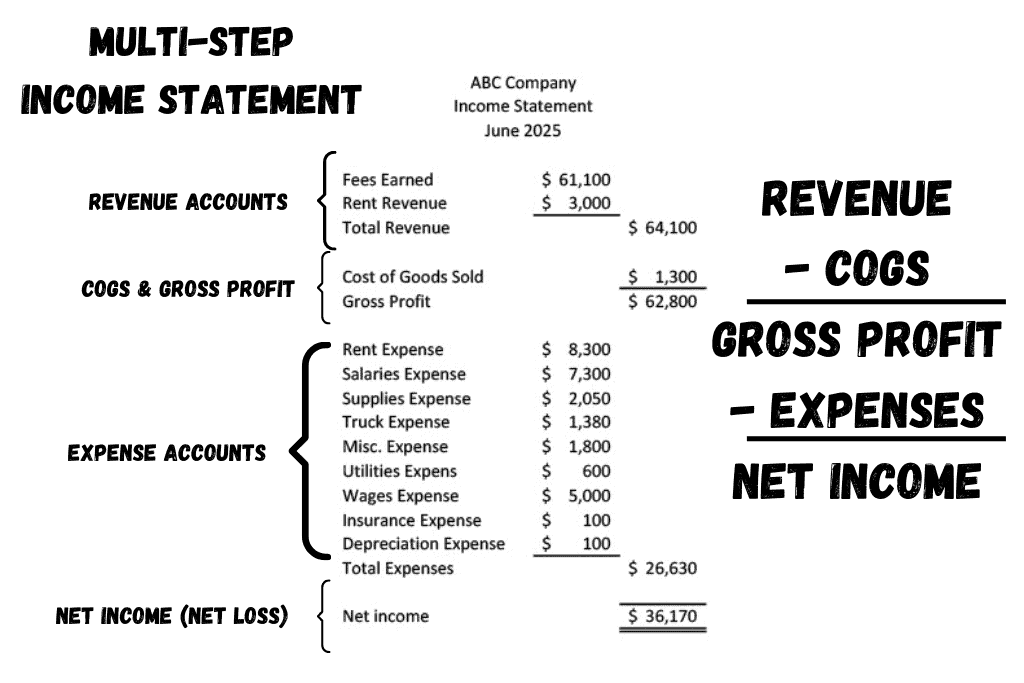
For example, the following company has Revenues of $64,100 and Cost of Goods Sold of $1,300. The difference between the two is Gross Profit. [$64,100 – $1,300 = $62,800] Gross Profit measures the profitability of the product or service being sold to customers. It ignores all the other expenses involved in running a business.
Those other expenses are listed below Gross Profit and represent all the general operating costs of running a business. When total of all the operating expenses are subtracted from Gross Profit, this gives the Net Income or Profit for the business during that period of time.
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (or Cost of Merchandise Sold)
Net Income = Gross Profit – Expenses
What Does Net Income Mean?
When a company has Net Income, it means the company is operating at a profit (revenue is greater than expenses.) When a company has a Net Loss, it means the company is operating at a loss (expenses are greater than revenue.)
For more information about Cost of Goods Sold and Cost of Merchandise Sold, check out this Accounting Student Guide:
-
Understanding Financial Statements | Accounting Student Guide
What is a Financial Statement? Financial Statements are a set of reports summarizing the activities of a business or organization. Much like a series of x-rays shows different views of
-
Accounting for a Merchandising Business | Accounting Student Guide
What is a Merchandising Business? A merchandising business is a business that purchases goods and re-sells the goods to its customers. Examples of merchandising businesses are Amazon and Wal-mart. A
-
Financial Statement Analysis | Accounting Student Guide
Financial Statements offer great insights into the financial health and operating efficiency of businesses and organizations. The reports are used both internally and externally. Internally, financial statements are used for
-
What is Cash Over and Short?
Cash Over and Short is an income statement account used to track differences in cash collections from what is expected and what is actual. It is used in businesses that
-
What is the Difference Between Permanent and Temporary Accounts?
In accounting, Permanent accounts carry a balance from one month to the next. Temporary accounts are zeroed out at the end of each month. Permanent accounts are the balance sheet
-
What is the Difference Between Periodic and Perpetual Inventory?
For a merchandising business, one of the most important success factors is the management of inventory. Because the cost and tracking of inventory is so critical, decisions made about inventory

